|
|
Headline |
|
Arthritis
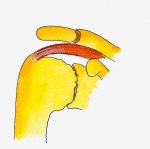
There are two main joints in the shoulder. The first is between the head of the arm bone (humerus) and the socket (glenoid) called the glenohumeral joint. The second joint is between the collar bone (clavicle) & the tip of the shoulder blade (acromion) called the acromio-clavicular joint. In this section the arthritis of the glenohumeral joint is discussed. The pathologies of acromio-clavicular joint is discussed here. |
What are the causes of Arthritis?
There are 3 main types of arthritis involving the shoulder joint.
- Osteoarthitis – age related arthritis due to excessive wear & tear
- Inflammatory arthritis like Rheumatoid arthritis – involves any age group. Mostly involves multiple joints
- Post-traumatic arthritis – develops after frature or repeated dislocation of the shoulder
Who gets it?
Oateoarthritis is usually seen in patients over the age of 50. The inflammatory arthritis as mentioned above can affect any age group. Post-traumatic arthritis affects younger patients. Post traumatic arthritis may accelerate the age related arthritis.
What are the symptoms?
The predominat symptom is pain. Pain may be related to activity. Pain also progressive worsens & in severe cases it may cause night and rest pain. In addition to pain patients may experience limitation of movements.
What investigations are required?
X-rays are sufficient to diagnose arthritis. Sometimes additional investigations such as CT scan, ultrasound scan or MR scan may be required to obtain additional information before surgery.
Treatment
Non-operative measures may be used in patients at the early stages of the disease. These include activity modification (avoid activities that cause pain), anti-inflammatory tablets, injections, physiotherapy, heat treatment and dietary supplements such as Glocosamine and chondroitin sulphate (these dietary supplements may not work for everyone & may only be effective in the early stages of the disease). One must consult with his / her GP before commencing on any medication.
Treatment of the Glenoid surface
 |
 |
 |
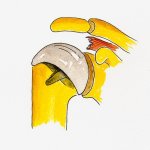
Glenoid resurfacing |
Glenoid microfracture |
Glenoid microfracture |
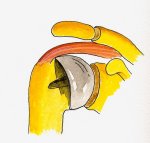
Surgery may be required if the non-operative measures fail. These vary from surface replacement where the bone is preserved. It is like shaving the arthritic joint & replacing with a metal cap (surface replacement).
Treatment options with intact cuff Treatment options without Treatment options without intact cuff
 |
 |
 |
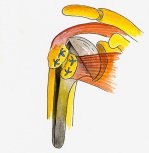 |
Sometimes when the disease is advanced it may not be possible to perform surface replacement, in which case a stemmed joint replacement is done. In some circumstances where there is arthritis and complete & irreparable cuff tears are noted your surgeon may consider what is called a reverse shoulder replacement. You may wish to discuss with your surgeon the various treatment options.
Surgical treatment is generally very effective is pain control and also restoring movement and function in the shoulder.
Post operation physiotherapy